-
1 система кабельных коробов
система кабельных коробов
Система замкнутых оболочек, состоящих из основания (корпуса) и съемной крышки, предназначенная дляполного заключения в себяпрокладки внутри неё изолированных проводов, кабелей, шнуров и (или) для размещения другого электрического оборудования, включая оборудование информационных технологий.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
система кабельных коробов
Система замкнутых оболочек, состоящих из корпуса со съемной или открывающейся крышкой, предназначенная для прокладки внутри нее изолированных проводов, кабелей и шнуров и/или для размещения другого электрооборудования.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61084-1 2007]
кабельнесущая система
Система закрытых оболочек, допускающая размещение изолированных проводов на базе подвижных поверхностей и предназначенная для полной защиты изолированных проводов, кабелей, шнуров, а также для размещения другого электрооборудования.
система кабельных коробов
Система закрываемых полых конструкций, состоящая из основания (корпуса) и съемной крышки, предназначенная для прокладки внутри них и защиты от механических повреждений кабелей, шнуров, изолированных проводов и (или) для размещения другого электрического оборудования, включая оборудование информационных технологий.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
Примечание. Синим цветом обозначен вариант, предлагаемый автором карточки.EN
cable trunking system
a system of closed enclosures comprising a base with a removable cover, intended for the complete surrounding of insulated conductors, cables, cords and/or for the accommodation of other electrical accessories
Source: 826-06-04 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-34]
cable trunking system
system of closed enclosures comprising a base with a removable cover, intended for the complete surrounding of insulated conductors, cables, cords and/or for the accommodation of other electric equipment including information technology equipment
Source: 442-02-34 MOD
[IEV number 826-15-04]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
système de goulottes
ensemble d'enveloppes fermées munies d'un fond avec un couvercle amovible et destiné à la protection complète de conducteurs isolés et de câbles, ou au logement d'autre petit appareillage électrique
Source: 826-06-04 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-34]
système de goulottes, m
ensemble d'enveloppes fermées, munies d'un fond avec un couvercle amovible et destiné à la protection complète des conducteurs isolés et des câbles et/ou au logement d'autres matériels électriques y compris des matériels de traitement de l'information
Source: 442-02-34 MOD
[IEV number 826-15-04]Обратите внимание!
Различают два вида систем кабельных коробов:
1) (просто) система кабельных коробов (cable trunking system) - система любого сечения, но обязательно с крышкой;
2) система специальных кабельных коробов (cable ducting system) - система некруглого сечения и без крышек.
Примечание. В ПУЭ короб без крышки называется глухой короб (см. кабельный короб)
[Автор карточки]
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Raceways shall be one- or two-piece design with base and snap-on cover, or three-piece design with base and two snap-on covers which snap side by side on a common base.
[Legrand/Wiremold. SECTION 16130 RACEWAY AND BOXES]В состав поставки входят специальные (глухие) кабельные короба, а также кабельные короба, состоящие из основания и защелкивающейся крышки, или из основания и двух защелкивающихся крышек.
[Перевод Интент]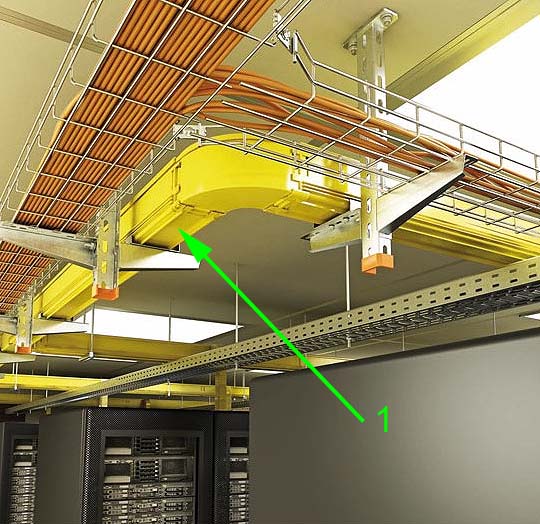
1 - Система кабельных коробов
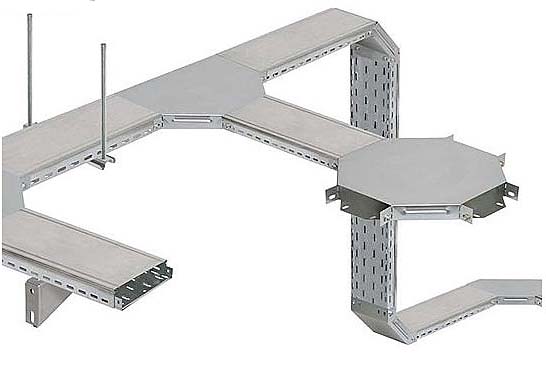
Система кабельных коробов
Система кабельных коробов
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1) - мнение автора карточкиТематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > система кабельных коробов
-
2 длительный допустимый ток
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > длительный допустимый ток
См. также в других словарях:
Cable barrier — Cable barrier, sometimes referred to as guard cable, is a type of roadside or median barrier. It consists of steel wire ropes mounted on weak posts. As is the case with any roadside barrier, its primary purpose is to prevent a vehicle from… … Wikipedia
Design on a Dime — Genre Reality, Home improvement Country of origin United States Language(s) English Production Running time 30 minutes … Wikipedia
Cable colors — are a set of color codes used in making fabrics with specific shades. The cable colors were created by The Color Association of the United States. The codes are kept in a book called the Standard Color Reference of America, which is kept by the… … Wikipedia
Design Suites Hotel Buenos Aires (Buenos Aires) — Design Suites Hotel Buenos Aires country: Argentina, city: Buenos Aires (City Centre) Design Suites Hotel Buenos Aires Location Located in Buenos Aires city center and a couple of blocks away from Santa Fe and Callao shopping district.Rooms The… … International hotels
Cable-stayed bridge — BridgeTypePix image title=The Rio Antirio bridge in Greece type name=Cable stayed bridge sibling names=None descendent names=Side spar cable stayed bridge, Self anchored suspension bridge, cantilever spar cable stayed bridge ancestor… … Wikipedia
Cable tie — Assortment of cable ties A cable tie, also known as a zip tie or tie wrap, is a type of fastener, especially for binding several electronic cables or wires together and to organize cables and wires. Contents … Wikipedia
Cable Liner — The Cable Liner and Cable Liner Shuttle is a range of automated people mover (APM) products designed by DCC Doppelmayr Cable Car for use at airports, in city centres, intermodal passenger transport connections, park and ride facilities, campuses … Wikipedia
Cable — For other uses, see Cable (disambiguation). 6 inch (15 cm) outside diameter, oil cooled cables, traversing the Grand Coulee Dam throughout. An example of a heavy cable for power transmission … Wikipedia
Cable modem — Motorola SurfBoard SBV6120E EuroDOCSIS 3.0 cable modem A cable modem is a type of network bridge and modem that provides bi directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a HFC and RFoG infrastructure. Cable modems are primarily… … Wikipedia
cable — cablelike, adj. /kay beuhl/, n., v., cabled, cabling. n. 1. a heavy, strong rope. 2. a very strong rope made of strands of metal wire, as used to support cable cars or suspension bridges. 3. a cord of metal wire used to operate or pull a… … Universalium
Cable — /kay beuhl/, n. George Washington, 1844 1925, U.S. novelist and short story writer. * * * (as used in expressions) Cable News Network cable modem cable structure cable television coaxial cable * * * ▪ electronics … Universalium
